Understanding CNC Spindle Maintenance is vital. Proper care ensures machines work efficiently. This blog shares best practices. Readers gain insights into optimal performance. Maintenance knowledge is power. Elevate machine care with expert tips.

A CNC spindle, part of Computer Numerical Control machinery, transforms digital instructions into precise movements. Key components include bearings, shafts, and the housing. Essential RPM (Revolutions per Minute) values range from 8,000 to 30,000, determining material removal rates. Bearings, often ceramic or steel, ensure smooth operation.
Proper lubrication, vital for longevity, prevents overheating. Regular maintenance checks, crucial for optimum performance, detect wear and tear early. Ensure you replace damaged parts promptly. By understanding these basics, one ensures the longevity and efficiency of the CNC machinery. Proper maintenance ensures accurate, efficient operations every time.
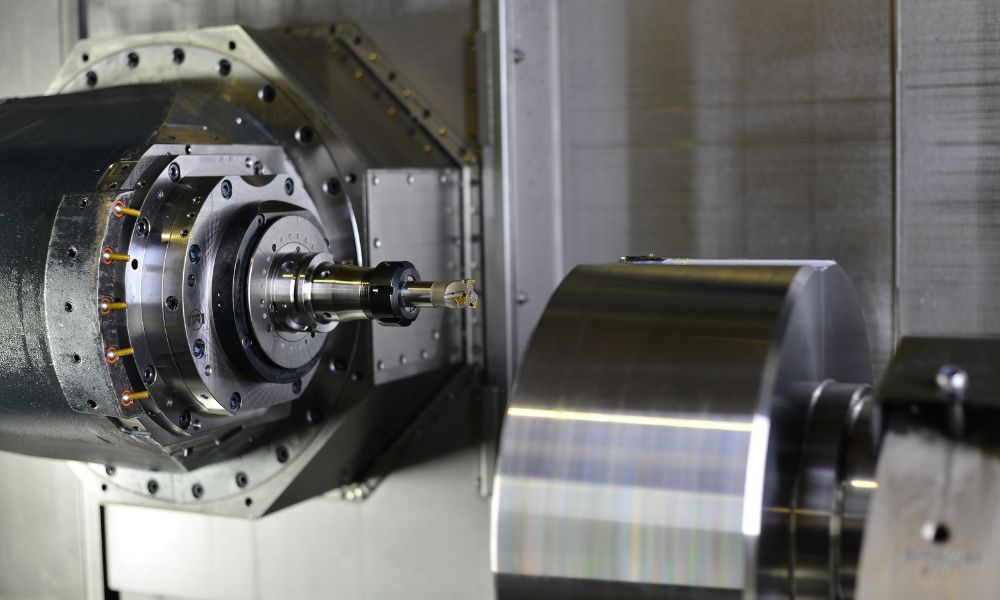

In CNC Spindle Maintenance, RPM (revolutions per minutes) matters. Maintaining optimal RPM ensures precise cuts. Bearings, crucial for smooth rotation, need regular checks.
Grease lubrication extends bearing life. Over time, wear causes decreased RPM. Regular maintenance prevents such wear. Always monitor spindle vibrations. Excessive vibrations indicate issues.
The tool holder's precision affects machining accuracy. BT, CAT, and HSK are common holder types. Each requires specific maintenance steps. Clamping force is vital for secure holding.
Over time, retention knobs loosen. Periodically check and tighten them. Clean tapers regularly for better contact. A clean taper prevents slipping. Ensure collets remain damage-free. Replace worn-out collets promptly.
Speed directly impacts machining outcomes. Variable frequency drives (VFDs) regulate spindle speed. Regularly inspect VFDs for optimal performance. Dust and debris affect speed sensors.
Clean sensors maintain accurate speed readings. Monitoring amperage ensures consistent speed. Sudden amperage spikes indicate problems. Timely intervention prevents further damage.
Torque affects cutting force. Insufficient torque leads to inefficient cuts. Regularly measure spindle torques. Use dynamometers for accurate readings. Ensure drive belts remain tensioned.
Loose belts cause torque loss. Replace worn-out belts to maintain torque. Monitor motor health, as it influences torque. A well-maintained motor delivers consistent torque.
Automatic tool changers (ATCs) increase efficiency. However, ATCs requires meticulous maintenance. Check carousel alignment for smooth operation. Sensors detect tool presence.
Clean sensors avoid false readings. Regularly lubricate moving parts. Lubrication prevents wear in ATCs. Ensure pneumatic systems remain leak-free. Air leaks hinder tool changing efficiency.
Coolant cools and lubricates cuts. Flow rate consistency is essential. Clogged nozzles reduce flow rates. Regularly clean coolant nozzles. Monitor coolant concentration levels.
Adjust levels for optimal performance. Ensure pumps operate efficiently. A malfunctioning pump disrupts coolant supply. Use filters to keep coolant clean. Replace filters when they become clogged.
Bearings play a central role. They allow the spindle to rotate smoothly. Proper lubrication extends their life. Over time, bearings wear out. Regular checks prevent unexpected failures.
Signs of wear include unusual noise and heat. RPM (revolutions per minute) affects bearing life. For optimal performance, replace them regularly. Neglect can lead to costly repairs. Always use the manufacturer's recommended bearings.
The drive motor powers the spindle. It determines speed and torque. A malfunctioning motor affects CNC operations. Regularly inspect for signs of wear. Keep the motor clean from debris. Overheating can damage the motor. Ensure adequate cooling during operations.
Monitor power consumption for irregularities. Address any changes in motor noise promptly. Efficiency drops with motor wear. Using OEM (original equipment manufacturer) parts ensures longevity.
The taper cone holds the tool securely. Precision is crucial for accurate machining. Any misalignment affects product quality. Regularly inspect for wear or damage. Clean the cone from any debris.
Use calibrated instruments for checks. Ensure the taper angle matches tool specifications. The BT30 and BT40 are common taper sizes. Periodic checks maintain machining accuracy.
The tool holder secures the cutting tool. A tight grip is essential for safety. Any slippage can lead to accidents. Regular inspection prevents potential hazards. Clean tool holders from coolant residues.
Use the correct pull stud for the spindle type. HSK and CAT are popular tool holder types. Ensure the tool holder's balance for best results.
The shaft, crucial in CNC spindle operations, rotates at RPMs ranging from 1,000 to 24,000. CNC techs monitor its balance for optimal performance. Bearings, often ceramic or steel, support the shaft. Proper lubrication ensures reduced friction.
Over time, debris might accumulate, demanding thorough cleaning. Regular maintenance checks combat wear and tear. Misalignments, if any, need prompt corrections.
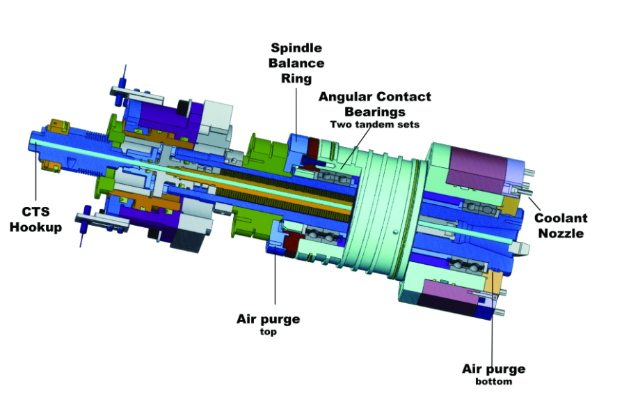
During CNC operations, spindles rotate at high RPMs. Proper maintenance ensures efficient material removal. Bearings, lubrication, and seals need regular checks.
A drop in RPM or increase in heat indicates issues. Neglecting maintenance leads to costly repairs. Always follow manufacturer guidelines. Using precision instruments like tachometers measures spindle speed. Regular inspection ensures longevity.
Accurate tool positioning hinges on spindle health. A well-maintained spindle ensures precise cuts. Alignment checks prevent machining errors. Misalignments often result from worn out bearings. Regularly lubricate spindle components.
A spindle's positioning accuracy depends on its health. Monitor for unusual noises or vibrations. Replace worn-out components promptly. Calibrate CNC machines after any spindle service. Documentation of maintenance activities is crucial.
Surface finishing quality links directly to spindle condition. A malfunctioning spindle produces uneven surfaces. Proper lubrication ensures smooth operations. Always clean and inspect spindles after use.
Debris can affect the finish. Maintenance routines improve product quality. Use micrometers to check surface finish consistency. Any deviation demands immediate spindle inspection.
Contouring involves creating complex shapes. A healthy spindle guarantees precise contouring. Maintenance checks include looking for tool deflections. Ensure that cooling systems work efficiently. Overheating affects contouring accuracy. Check spindle run-out with dial indicators.
Regularly update CNC software. Outdated software can affect contouring precision. Keep a log of all maintenance activities.
Drilling requires spindle stability. Regular maintenance avoids drill wander. Check the spindle's axial and radial play. Any play affects hole accuracy. Clean and lubricate the spindle after every operation.
Drilling speeds vary, so monitor spindle health. Using depth micrometers checks hole depths. Routine maintenance ensures hole consistency.
For detailed engravings, spindle precision is key. Engraving details can be as small as 0.001 inches. Spindle imbalance affects engraving quality. Regularly inspect for wear and tear.
Ensure that cooling systems are functioning. Overheating can warp engravings. Document all maintenance for accountability. Proper spindle care ensures crisp engravings. Always follow recommended maintenance schedules.
Proper CNC Spindle Maintenance ensures quiet operation. Without maintenance, bearings degrade, causing loud sounds. High decibels indicate worn components. Changing bearings reduces noise levels.
Vibrations compromise precision. Misaligned bearings or a damaged shaft can lead to them. Using high-precision tools, experts detect and correct imbalances. Regular inspections prevent severe damage.
Precision matters in CNC operations. Wear and tear affects spindle alignment. Calibration ensures perfect alignment. Measure parts dimensions after machining. Any deviations signal the need for spindle adjustments.
Spindles shouldn't get too hot. Coolant systems keep temperatures stable. Blocked vents or degraded seals increase heat. Invest in high-quality coolants. Regularly check temperature gauges.
In CNC operations, speed is essential. Aging components slow down spindles. Regular lubrication ensures quick spindle reactions. Replace worn belts and pulleys to improve responsiveness.
When machining, a spindle's precision matters. Tool deflection can ruin that precision. If a CNC machine's cutter bends away from the set path, your product quality suffers. Regular calibration and alignment ensure minimal deflection.
Measure deviations using dial indicators. Adjust CNC parameters like feed rate and RPM. Proper maintenance and correct tool selection reduce tool deflection risks. Always consult the machine's manual for specifications.
Spindle stalling spells trouble. Often, overload causes a spindle to stall. Overload happens when the spindle's motor exceeds its torque capacity. Observing the machine's amperage can prevent stalling.
Moreover, spindle lubrication is paramount. Clean and lubricate regularly. Utilize the correct grade of lubricant. Properly maintained spindles rarely stall. Heed warning signs.
Effective CNC Spindle Maintenance demands regular checks. Daily inspections ensure optimal performance. Monitor spindle temperature; high temperatures indicate issues. Regularly clean air purges lines.
Blocked lines cause overheating. Every 500 hours, change the air filter. Every 2000 hours, change the spindle's coolant. Consistency in checks ensures longevity and efficiency.
Bearings play a crucial role in spindle function. Worn-out bearings compromise spindle accuracy. Listen for unusual noises; they indicate bearing issues. Use thermal cameras to check bearing temperatures.
Excessive heat suggests malfunction. Replace bearings at regular intervals. Opt for high-quality bearings. Ensure lubrication is optimal for peak bearing performance.
Drive belts transfer motor power to the spindle. Correct belt tension is essential for efficient transfer. Too loose Power transfer decreases. Use a tension meter to measure belt tension.
Adjust tension as per manufacturer guidelines. Regularly inspect belts for wear. Replace worn or damaged belts promptly. Proper belt care ensures consistent spindle speed and accuracy.
In CNC spindle maintenance, optimal lubrication is vital. Insufficient lubrication results in high friction. Consequently, spindles overheat, causing premature wear. Regular checks ensure proper oil levels.
Lubricants with high viscosity reduce wear. Moreover, ISO VG 22 oil suits most CNC spindles. Always monitor oil for contamination. Clean oil guarantees spindle longevity.
A functional cooling system is crucial for spindle performance. Elevated temperatures damage spindle bearings. Thus, a spindle's RPM can drop, reducing efficiency. Regularly inspect coolant flow.
Blocked channels restrict cooling. Additionally, maintaining 68°F (20°C) coolant temperature is optimal. Furthermore, ensure a steady flow of 0.8 GPM for efficient cooling.
Precision in CNC machines hinges on tool holders. Worn-out tool holders affect accuracy. Regular inspections detect early wear signs. High-speed operations require balanced holders. An imbalance leads to vibrations.
Replace tool holders after 10,000 hours for best results. ATC cycles also influence wear rate. Notably, HSK tool holders offer better clamping force. Proper maintenance ensures machining accuracy.
Proper alignment is crucial. Misalignment can lead to inaccurate cuts. Use a dial test indicator for alignment checks. Perform this check every 600 hours. Proper spindle alignment guarantees accurate machining.
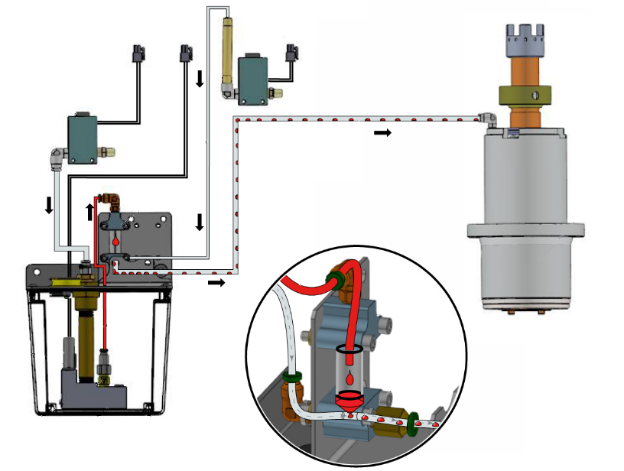
In CNC Spindle Maintenance, grease stands out. Grease offers consistent lubrication. Over time, spindles benefit from grease application. Regular maintenance uses NLGI grade 2 grease.
Grease ensures reduced friction. Proper grease application prevents wear. Every spindle type has specific grease needs. Consult the manufacturer's guide for details.
Oil remains vital for spindle health. High-speed spindles often require oil. Oil offers rapid cooling benefits. Regular maintenance ensures the right oil viscosity. Spindle bearings thrive with oil lubrication. Oil circulates and removes heat. Proper oil selection is essential. Always consider spindle speed and bearing type.
Synthetic fluids offer advanced protection. Chemically engineered, they resist breakdown. In high-temperature conditions, synthetic outperforms. For precision machinery, synthetic is a top choice. Unlike natural oils, synthetic offers consistent quality. For optimal spindle performance, consider synthetic fluids.
For quick applications, aerosol sprays help. Aerosol delivers lubrication to tight spots. In CNC machines, aerosol reaches inaccessible areas. Ensure proper ventilation when using aerosols. Aerosol sprays offer convenience and precision.
PTFE, known as Teflon, serves spindles well. PTFE compounds reduce friction superbly. They provide a protective layer on spindles. High temperatures don't degrade PTFE easily.
For prolonged spindle life, PTFE compounds are invaluable. In harsh conditions, PTFE ensures smooth operations.
Graphite lubricants cater to extreme conditions. Graphite withstands high temperatures. In CNC Spindle Maintenance, graphite protects against wear. Solid lubricants, like graphite, offer unique advantages. They ensure consistent operation even in high-load scenarios.
Proper lubrication ensures CNC spindle parts move smoothly. Over time, friction between moving parts increases. Too much friction causes wear. Lubrication reduces that friction. For CNC machines, use ISO VG32 or ISO VG68 oil.
Regularly check the oil's level. Replace old oil with fresh oil. Every 500 operating hours, conduct a thorough check. Keeping parts well-lubricated extends their lifespan.
Always follow the manufacturer's guidelines. Remember, a well-maintained spindle performs better. Always consult the machine manual for specific lubrication guidelines.
Heat damages CNC spindle components. Effective cooling prevents this damage. Spindle motors generate heat during operations. Excess heat affects precision and accuracy. Use coolants like water-soluble oils or synthetic fluids.
Ensure proper coolant flow during operations. Adjust the flow rate to 20-40 liters per minute. Monitor the spindle's temperature with infrared sensors.
Too high temperatures indicate issues. Address them immediately. Proper temperature control keeps the spindle in top condition.
Less friction equals smoother operation. High-speed spindles need grease-based lubricants. Grease reduces friction between moving parts. Bearings last longer with reduced friction. Use NLGI grade 2 grease for the best results.
Moreover, regular inspections detect friction issues early. Reduced friction ensures the spindle operates at peak efficiency.
In CNC Spindle Maintenance, rust harms spindles. Grease stops rust. Every 30 hours, add grease. Use ISO 32 or ISO 68. Experts suggest HLPD oils.
Too much rust damages spindles. Proper maintenance saves money. Always check for rust signs. Use anti-corrosion products. Timely actions prolong spindle life.
Regular lubrication helps spindles. Experts recommend every 50 hours. Use correct lubrication tools. Follow manufacturer guidelines.
Using MO2T or MO4T types is crucial. Schedule ensures smooth operation. Proper timing avoids future issues.
Volume matters in lubrication. Too little’s or too much harms. Use 20ml to 25ml for standard spindles. High-speed ones need 10ml to 15ml always use calibrated tools. Following standards ensures safety. Remember, over-lubrication causes waste.
Uniform grease distribution is key. Avoid clumps. Use brushes or spatulas. Ensure spindle surfaces get covered. Uneven spots lead to wear. Regular checks help identify gaps. Proper tools ensure even spread. Uniformity extends spindle life.
Keep spindles clean. Dirt affects performance. Before lubrication, remove old grease. Use cotton cloths or specialized wipes. Avoid using water. High-quality cleaning agents help. Cleanliness boosts efficiency. Clean spindles work best.
Vibration analysis plays a crucial role in CNC spindle health. By measuring frequencies, experts identify early wear and tear. RPM (revolutions per minute) values guide technicians. Spindle errors detected early save time and money.
Consistent checks ensure optimal machine function. Precise tools like accelerometers capture spindle imbalances. Swift action prevents further damage.
Misalignment in CNC machines affects precision. Using dial indicators, experts detect slight shifts. Deviations from set parameters highlight misalignment. Alignment checks occur during regular maintenance.
When axles skew, product quality drops. Technicians rectify issues using specific procedures. Proper alignment ensures longevity and accuracy. Tools like laser aligners provide exact measurements.
Bearings are central to CNC spindle function. Over time, wear impacts bearing health. Lubrication levels require regular monitoring. Insufficient grease leads to friction. High temperatures indicate bearing issues.
Technicians use thermal cameras for checks. Proper maintenance ensures smooth rotation. Replacing old bearings extends spindle life. Regular checks prevent unexpected machine halts.
An unbalanced tool affects performance. Vibration analysis detects imbalances. Ensure tools are balanced for optimal spindle operations. Use balancing equipment for precision.
Imbalances can shorten spindle lifespan. Regular checks maintain tool balance and ensure efficient CNC operations.
|
Parameter |
Importance (1-10) |
Frequency Range (Hz) |
Common Issues |
Impact on Spindle Health (%) |
Mitigation Techniques |
Measurement Tools |
|
Early Damage Detection |
9 |
10-1000 |
Cracks, Wear |
75 |
Regular Inspections |
Accelerometers |
|
Misalignment Identification |
8 |
20-500 |
Offset, Angular |
60 |
Laser Alignment |
Vibration Analyzers |
|
Bearing Condition |
10 |
50-2000 |
Pitting, Contamination |
80 |
Lubrication, Replacement |
Stethoscopes |
|
Tool Balance |
7 |
100-1500 |
Unbalance, Wobbling |
50 |
Dynamic Balancing |
Balancing Machines |
Table on Vibration Analysis And Its Role In Spindle Health!
Modern CNC machines utilize advanced laser systems for spindle alignment. Second, these lasers provide micro-level accuracy, ensuring optimal performance. In fact, incorrect alignment can decrease tool life by 10% to 50%.
Conducting geometric tests on spindles identifies inconsistencies. For instance, CNC professionals use high-precision instruments, like CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machines), during this process. Indeed, geometric inconsistencies can cause a 5% decrease in dimensional accuracy.
Calibration of the rotary axis optimizes machine precision. Notably, CNC experts recommend calibrating every six months. Equipment like RACs (Rotary Axis Calibrators) plays a pivotal role here. In fact, proper calibration enhances spindle lifespan by up to 30%.
Verifying spindle straightness remains paramount. For example, deviations, even as minute as 0.005mm, can affect product quality. Indeed, using tools like straight edges and precision levels achieves this.
Finally, pitch error impacts accuracy and surface finish. CNC professionals employ specialized devices, like linear encoders, for this task. Correcting pitch errors can improve surface finish quality by up to 15%.
Before starting, always inspect your tool holder. Damaged holders impact spindle balance. Replace worn-out holders promptly.
Proper dynamic balancing enhances spindle performance. Every spindle needs regular dynamic balance checks. Neglect leads to reduced tool life.
Just like dynamic, static balance matters. Precision in static balance ensures consistent cuts. A spindle with off-balance statics hampers precision.
Test your spindle at various RPMs. Optimal operation requires a broad RPM range test. Such tests detect inconsistencies in speed.
High vibrations indicate issues. Use a reliable vibration meter for accurate readings. Address high readings immediately for longevity.
|
Criteria/Methods |
Description |
Tools/Instruments Used |
Accuracy Level |
Test Duration |
Cost |
Application Scenarios |
|
Vibration Metering |
Measures spindle vibrations |
Vibration meter |
High |
5-10 minutes |
Medium |
Initial diagnosis, maintenance |
|
Rpm Range Test |
Tests spindle at various RPMs |
Tachometer |
Medium |
10-15 minutes |
Low |
Speed performance verification |
|
Static Balancing |
Balances spindle without rotation |
Balancing stand |
Medium |
20-30 minutes |
Low |
When spindle isn't rotating |
|
Dynamic Balancing |
Balances spindle during rotation |
Balancing machine |
High |
30-45 minutes |
High |
When spindle is in operation |
|
Tool Holder Check |
Ensures tool holder is correctly fitted |
Inspection tools |
Medium |
5-10 minutes |
Low |
Before starting spindle |
Table On Balancing The Spindle For Optimal Output!
Proper CNC spindle maintenance is critical. Every machine needs regular care. Top performance comes from best practices. Readers now have the tools for success. For advanced support, visit CNCYANGSEN. Commit to excellence in CNC care. Elevate machine longevity and precision. Your machine's future depends on today's care.