In CNC Precision Machining, experts shape metal with great care. They turn rough pieces into parts for machines, tools, and more. This blog talks about how they do it. It looks at the steps, skills, and tools they use. Readers will learn about making things with precision and skill.
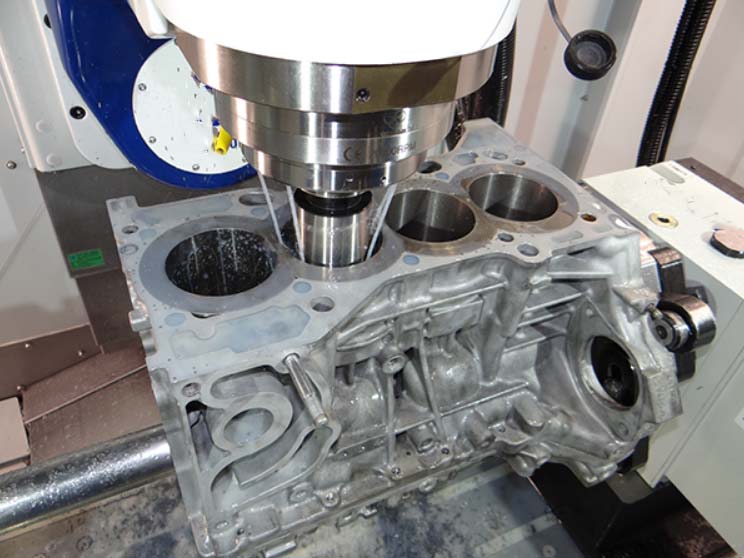

Central to CNC precision machining, milling machines shape metals and plastics. They use rotary cutters for precise cuts. Sizes range from small, bench-mounted devices to larger, room-sized equipment. Their parts include the cutter, spindle, and worktable. Milling machines are essential in manufacturing.
Lathe in CNC precision machining turn material. As the workpiece spins, the machine shapes it. Lathes work on metal and wood. Key parts are the chuck, spindle, and tailstock. They vary in size. Lathes are crucial for cylindrical parts.
CNC routers cut hard materials like wood, steel, and plastics. They carve, shape, and engrave. Routers use different bits for various cuts. They come in sizes from small desktop units to large industrial machines. Routers are vital in woodworking and metalworking.
Grinders in CNC machining shape metal through abrasion. They use a rotating wheel. Grinders polish, cut, and finish metals. Key parts include the grinding wheel, table, and chuck.
Sizes range from small hand-held units to larger industrial models. Grinders are important for precise metalwork.
Plasma cutters in CNC machining slice through metal using plasma. They handle steel, brass, and other metals. Cutters vary from portable to heavy-duty industrial units.
Key components are the cutting torch and power supply. Plasma cutters are crucial for metal fabrication.
EDM uses electrical sparks to shape materials. It works on hard metals. EDM machines include the electrode and dielectric fluid. They range from small bench top units to large industrial machines. EDM is key in intricate metal shaping.
In CNC Precision Machining, the spindle plays a crucial role. It holds and rotates the cutting tools. This part works under high speed. The spindle's power and speed are key. They define the machine's cutting capabilities. High speed ensures efficient, precise cuts. Strong spindles handle tough materials. It’s a core component.
The chuck is vital too. It holds the workpiece securely. During machining, the chuck must grip firmly. This ensures accurate, safe operations.
A loose chuck causes errors or accidents. Chucks vary in size and type. Each suits different workpieces. Precision in machining starts with a well-chosen, well-maintained chuck.
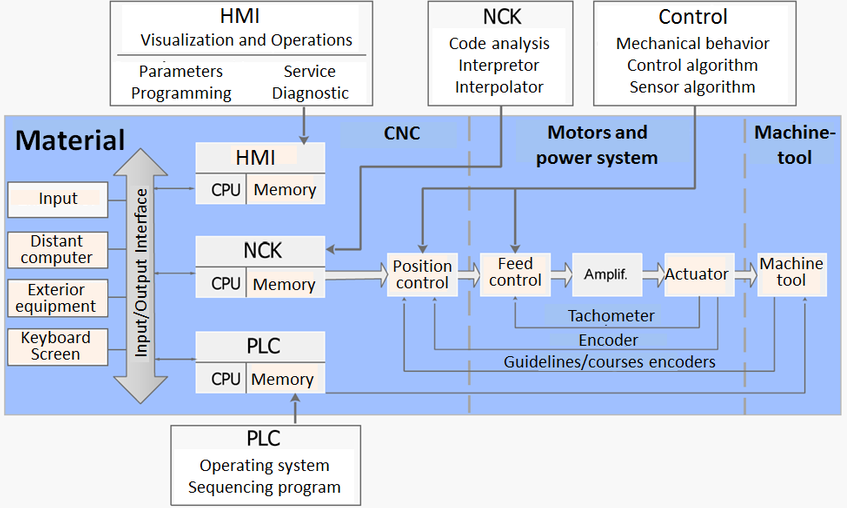
The controller is the machine's brain. It interprets digital instructions. Then, it directs the machine's movements. Precision machining relies on accurate controller commands. Even small errors in the controller affect the final product. Thus, a reliable controller is key. It ensures the machine follows exact paths, cuts precisely.
In CNC Precision Machining, the bed holds all major parts. It's the base. Made of heavy, rigid material, it supports operations. High precision relies on its stability. Accuracy in machining depends on a solid, unwavering bed.
Crucial for CNC Precision Machining, this system controls temperature. During cutting, heat builds up. The coolant system prevents overheating. It extends tool life. It ensures smooth, precise cuts. A well-maintained coolant system is key for effective machining.
This part holds various tools. In CNC machining, it rotates. It brings the needed tool into position. Quick, accurate tool changes are vital. The tool turret's efficiency boosts productivity. It's essential for complex, varied machining tasks.
These motors move the machine parts. Precision in movement is crucial. Axis motors control speed and position. They ensure accuracy in CNC machining. Fine-tuned axis motors result in precise, high-quality products. They are the heart of machine motion control.
Aluminum in CNC precision machining brings strength without weight. Linear rails made of aluminum stand out. They offer smooth motion for machinery. Components like carriages and guide rails benefit. The result is Enhanced precision in applications.
Consider steel, a cornerstone in CNC machining. Its linear rails exude robustness. They withstand high loads. Precision tools demand such steel qualities. Steel linear rails are essential. They support heavy-duty machining with reliability.
Brass, often chosen for its machinability, plays a vital role. In CNC precision machining, brass linear rails shine. They reduce friction. Plus, they resist corrosion. This makes them ideal for specific machining tasks. Their unique properties are invaluable.
Titanium stands out for its strength-to-weight ratio. In CNC machining, titanium linear rails are noteworthy. They resist wear and tear. Even under stress, they perform. These rails are crucial for high-performance applications. They bring durability and precision together.
Polycarbonate offers unique benefits. In CNC machining, its linear rails are lightweight yet strong. They suit applications needing transparency and resilience. These rails broaden the scope of CNC machining possibilities. They blend strength with versatility.
Acrylic is another key player. In CNC precision machining, acrylic linear rails have a place. They provide clarity and strength. Their impact resistance is notable.
For certain design-driven projects, they are the preferred choice. Their functionality meets aesthetic needs.
Nylon's role is undeniable. Nylon linear rails in CNC machining offer low friction. They are wear-resistant. Their light weight is an advantage in certain machinery. These rails enhance the performance of various CNC applications. They are practical and efficient.

In CNC Precision Machining, design starts with a clear plan. Imagine a blueprint for a complex part. Each line and curve is crucial. There's a focus on dimensions, like 10mm edges or 3cm holes. Think of materials too, maybe aluminum or steel. Tools like CAD software are key.
Programming transforms design into commands. For CNC Precision Machining, code is the language. It guides machines like a skilled conductor. Each command adjusts movements, from 2-inch shifts to precise 45-degree turns. The program is a roadmap, leading to flawless auto-parts.
Setup is setting the stage. The machine gets ready. Tools are picked, like specific drills for 5mm holes. Materials, perhaps a 2-foot steel block, are secured. The machine is calibrated. Every part, every tool, must be in the right place. Precision is the mantra here.
Execution - where action happens. The machine hums to life. It follows the programmed path. Metal cuts like butter. Chips fly. There's a dance of parts - a drill a cutter there. The machine shapes the material, following every programmed command.
Inspection is the quality check. It's about details. Gauges and calipers come out. Measurements are taken, down to the last 0.01mm. Each angle and curve is scrutinized. The goal is Perfection. If there’s an error, even a tiny one, it’s back to step one.
Finishing adds the final touch. It's like a painter's last stroke. Surfaces are smoothed, edges are polished. Sometimes there's painting or coating. It's about aesthetics and protection. The part, once a raw material, now shines, ready for the world.
Assembly - the culmination. Different parts, made with precision, come together. It's like a puzzle. Each piece fits just right. Screws, bolts, and welds join them. The final product stands ready, a testament to the skill and precision of CNC Machining.
In CNC Precision Machining, tolerances stand as crucial markers. Every component demands exact measures. Imagine gears in a clock. Each must fit perfectly. Even a hair's breadth deviation could lead to failure. Precision in measurements, down to micrometers, ensures seamless functioning.
Dimensions form the framework of precision machining. Accurate lengths, widths, and heights are non-negotiable. Consider a surgeon's tools.
Each piece must match specific dimensions for successful surgery. Similarly, in CNC precision machining, precise dimensions guarantee the machine's effectiveness and reliability.
Material choice is a cornerstone. Different materials behave uniquely under stress. Steel and aluminum, for instance, vary in strength and flexibility.
Each project requires a careful selection of materials. Wrong choices can compromise the product's integrity and performance.
Geometric precision is pivotal. Every angle and curve must align accurately. Picture a puzzle. If one piece is off, the entire puzzle suffers. In CNC Precision Machining, even a slight error in geometry can derail an entire project.
The path tools take is vital. These paths dictate the machine's accuracy. A wrong turn can spell disaster. Think of a map.
If the route is wrong, the destination remains unreachable. Similarly, in precision machining, precise tool paths are the roadmap to success.
The surface finish is more than aesthetic. It’s about functionality. A smooth finish can mean less friction, longer life for parts. Imagine a slide. The smoother it is, the faster the ride. In CNC Precision Machining, a superior surface finish enhances the product's overall performance.

In CNC Precision Machining, toolpath creation is vital. CAM software plays a key role. It translates 3D models into instructions. These instructions guide CNC machines.
It's about precision. Each toolpath must be exact. The software considers factors like cutter shape and size. It plans paths for minimal waste and maximal efficiency.
Before actual cutting, CAM offers simulation. Imagine a virtual CNC machine. It mimics real operations. You see the tool moving. It carves through digital material.
The software predicts possible errors. Think collisions or tool wear. This step is crucial. It saves time and material. By simulating, you avoid costly mistakes in real CNC Precision Machining.
CAM software generates G-code. This is the language for CNC machines. The code instructs every move. It tells the machine where to cut, drill, or turn. Precision is non-negotiable.
One wrong command can ruin a part. CAM ensures each line of code is perfect. It turns complex designs into flawless products.
CAM doesn't just create toolpaths. It optimizes them. The software analyzes many paths. It chooses the best one. This means less time cutting. It also means less tool wear.
The goal is efficiency. Optimal paths save time and money. They produce better parts. CAM makes CNC machines work smarter.
CAM interfaces with CNC machines. It controls every aspect. These are all under CAM's command. The software adjusts in real-time. It responds to material differences.
It adapts to tool wear. CAM ensures that machines follow the plan perfectly. It's like an expert conductor leading an orchestra.
CAM integrates with design software. This creates a seamless workflow. Designers make a model. CAM turns it into reality. The two systems talk to each other.
They make sure the final product matches the design. This integration is essential. It bridges the gap between idea and physical object.
|
Aspect of CNC |
Role of CAM |
Benefits |
Limitations |
Key Terminology |
Technology Integration |
Industry Applications |
|
Simulation |
Visualizes machining process |
Prevents errors, Saves material |
May not account for all real-world variables |
Virtual machining, 3D simulation |
3D modeling software |
Manufacturing, Prototyping |
|
Code Generation |
Converts designs into machine code |
Streamlines production, Reduces manual programming |
Dependent on software compatibility |
G-code, Post-processing |
Software-to-hardware communication |
Electronics, Precision engineering |
|
Process Optimization |
Improves efficiency and speed |
Reduces time and costs, Enhances quality |
Needs continuous updates |
Feed rate, Cutting speed |
AI and Machine Learning for optimization |
Mass production, Custom manufacturing |
|
Machine Control |
Directs CNC machine actions |
Improves precision, Automates processes |
High dependence on software reliability |
CNC interface, Real-time control |
IoT for machine connectivity |
Robotics, Medical devices |
|
Design Integration |
Links design with manufacturing |
Seamless transition from design to production |
Requires compatible software systems |
CAD/CAM integration, Data transfer |
Cloud computing for data sharing |
Furniture, Mold making |
A Table On Role Of Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) In CNC!
In aerospace engineering, CNC Precision Machining crafts parts like turbine blades. The process involves exact measurements, often down to 0.0001 inches.
Titanium, a common material, demands precise tooling. Each part, from fuselage panels to engine components, showcases machining's precision. The industry values this accuracy for safety and performance.
For medical devices, CNC Precision Machining plays a crucial role. Surgeons rely on perfectly crafted instruments.
The machines produce items like joint replacements, each needing exact dimensions for patient fit. Stainless steel, known for its hygiene, is a preferred material. Such precision impacts lives, making the process invaluable in medicine.
In the automotive sector, CNC Precision Machining ensures reliability. Engine blocks and gearbox components need exact fits.
A typical car has over 30,000 parts, many machined to precise standards. Aluminum used for its light weight, demands careful handling. This precision underpins vehicle safety and efficiency.
Mold making through CNC Precision Machining shapes numerous industries. These molds create everything from bottle caps to automotive dashboards. Accuracy is key, as a slight error can render a mold unusable. Machining ensures each mold meets exact specifications, vital for mass production.
Prototyping is revolutionized by CNC Precision Machining. Prototypes for products like phones require exact dimensions.
The process allows rapid creation and alteration of designs, accelerating development. Materials range from plastics to metals, each needing specific machining parameters. This flexibility is essential for innovation.
In electronics, CNC Precision Machining produces components like circuit boards. Precision is crucial, as a minor flaw can cause a device to fail. The process handles materials like copper with care, ensuring functionality. These tiny, precise parts are the heart of modern electronics.
Custom machinery benefits greatly from CNC precision machining. Unique designs for industries like printing or textiles rely on customized parts.
These machines often require non-standard components, made to exact specifications. The process allows for such customization, meeting diverse industry needs.
The blog has shared deep insights into CNC Precision Machining. It has explained how skilled people use tools to shape metal finely. For those eager to dive deeper, visit CNCYANGSEN. Here, more knowledge waits, shedding light on this fascinating and precise world of manufacturing.