Delve deep into the realm of CNC Rotary Table technology. Uncover the essence of modern machining methods. This blog offers an authoritative exploration. Precision, efficiency, and innovation await your discovery.
Milling removes material from a workpiece. Engraving creates designs on a surface. In milling, cutters rotate. In engraving, tools etch patterns. Milling depth varies.
Engraving depth remains constant. Both need precision. But their goals differ. Milling shapes. Engraving decorates. Each has unique CNC settings.
Milling machines have a fixed table. A CNC Rotary Table rotates. This rotation aids in multi-sided machining. For intricate parts, rotation matters.
Milling usually goes horizontally. With rotation, milling can be multi-directional. Engraving remains surface-focused. It doesn't need table rotation like milling.
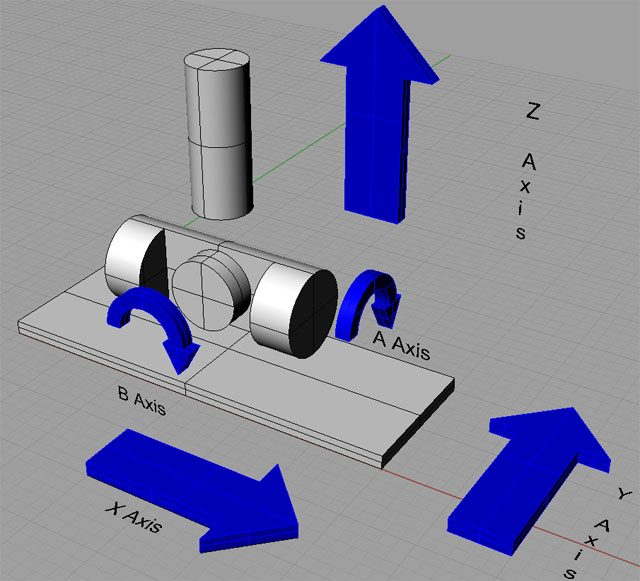
Milling machines move in X, Y, Z axes. Rotary tables add A, B, C axes. These extra axes aid in intricate machining. Milling requires depth control.
Engraving needs surface precision. Rotary tables aid both. But their significance shines in multi-axis milling.
In milling, workpieces need secure holding. Clamping ensures this. Strong clamps prevent movement. In engraving, clamps hold surfaces still.
Surface stability is key. For both milling and engraving, clamps are crucial. They ensure precision and control quality.
Motors drive CNC machines. Servo motors offer precision. CNC Milling Machine requires force. Servo motors provide that force. Engraving needs delicate movements. Servos offer those too. Their speed and accuracy benefit both processes. Their settings might differ.
CNC means Computer Numerical Control. The controller unit is the brain. For milling, it controls depth and speed. For engraving, it manages design and precision.
Both tasks need commands. The controller unit provides them. It interprets and executes them.
Machines need monitoring. Feedback systems provide this. They relay machine performance. Milling needs depth checks.
Engraving requires design accuracy checks. Feedback systems monitor these. They ensure the CNC Rotary Table works as needed.
Milling removes material with a rotating cutter. Engraving carves designs onto surfaces. In CNC Rotary Tables, drive trains manage the cutter's speed. RPM (revolutions per minute) figures vary, with typical CNC machines ranging from 1,000 to 24,000 RPM.
Speed matters: higher RPM for engraving lower for milling. Correct RPM ensures clean cuts. Check machine specs before starting.
Milling and engraving differ, yet both need accurate gears. CNC Rotary Table gears ensure exact movements. Milling needs robust gears for heavy cuts.
Engraving requires delicate, precise gears. GT or Gear Teeth numbers indicate gear size. Higher GT means larger gears, ideal for milling. For engraving, choose gears with lower GT. Prioritize gear quality for optimal results.
Tool paths guide milling and engraving actions. Milling follows paths to remove bulk material. Engraving paths are intricate for detailed designs. CNC software generates these paths.
Parameters like feed rate and depth affect the outcome. A 2mm depth might suit engraving, while 5mm suits milling. Adjust tool paths based on desired outcomes. Proper path planning ensures success.
In CNC machining, synchronization between axes is vital. Milling, a cutting process, shapes metal by removing parts. Engraving, on the other hand, carves designs onto surfaces.
To achieve accuracy, the CNC rotary table moves in harmony with other axes. Precise movements result in detailed work. CNC parameters like X, Y, and Z coordinate play a role in this synchronization.
G-Code, essential in CNC operations, directs machine actions. Now, while milling cuts material layers, engraving marks surfaces without cutting deep.
G-Code controls these functions. Proper integration ensures desired outcomes. Parameters like feed rate (FR) and spindle speed (SS) get determined through G-Code.
Adjusting tool positions is fundamental. Milling requires different depths than engraving.
Tool offsets help in these adjustments. Tools like end mills or engravers have specific offsets. Setting the right offset ensures precision. Parameters such as tool length (TL) and diameter (TD) guide these adjustments.
Holding workpieces securely is a must. Milling needs stability due to its force, while engraving and milling demands precision. Workholding solutions, like chucks and vises, offer this stability. They adapt based on workpiece size (WS) and shape. Proper workholding ensures error-free operations.
Monitoring machine operations provides advantages. In milling, material removal is watched. In engraving, design depth is the focus. Real-time feedback aids in immediate corrections.
Parameters, especially error rates (ER), are crucial for quality checks. Feedback systems, using sensors, give updates on these parameters.
Speed affects machining outcomes. Milling needs varied speeds based on material. Engraving requires consistency for clear designs. Spindle speed, measured in RPM (rotations per minute), is adjustable. Correct RPM settings, guided by material type (MT), ensure optimal results.
Connecting machines boosts efficiency. While milling shapes materials, engraving adds details. Interfacing allows these processes to work in tandem.
Integration methods, using protocols like RS-232 or Ethernet, enable this connection. Proper interfacing ensures smooth CNC rotary table operations.
Milling involves removing material from a workpiece. Conversely, engraving carves designs onto surfaces. In milling, a CNC machine moves in three dimensions. Engraving, on the other hand, focuses on surface detail.
Milling often requires robust cutting tools, whereas engraving tools tend to be finer. Both processes benefit from precise CNC rotary table control.
Milling carves away material. Engraving imprints or etches designs. While milling uses rotational cutting to form shapes, engraving employs fine tools for detailed work.
CNC machinery aids milling by providing 3D control. Engraving, in contrast, emphasizes surface nuances.
Milling and engraving serve distinct purposes. Milling removes material to shape objects. Engraving etches or imprints onto surfaces. Robust tools dominate milling, while engraving uses delicate tools.
Both rely on the precision of CNC tables. Proper clamping ensures workpiece stability.
In milling, cutting occurs across various angles to shape material. Engraving focuses on designs and patterns.
Milling tools cut and carve. Engraving tools delicately imprint. CNC rotary tables enhance angle control, optimizing both processes.
Milling processes shape materials using robust tools. Engraving, in contrast, employs finer tools for detail. Tools for milling are designed for cutting depth.
Engraving tools prioritize precision. A CNC rotary table's precision ensures optimal tool access.
Milling reshapes a workpiece by cutting away material. Engraving decorates or labels surfaces. Handling in milling requires secure placement. Engraving demands finesse and delicacy. CNC tables play a pivotal role in both, ensuring accurate workpiece management.
Precision remains paramount in milling and engraving. Milling reshapes objects, demanding exact measurements. Engraving requires detailed precision for designs.
CNC rotary tables offer exact positional control, crucial for both milling and engraving tasks.
Milling uses rotating tools to cut materials. Engraving employs a pointed tool to etch designs. Milling provides smoother surfaces. On a CNC Rotary Table, RPM settings influence the finish. High RPM values give finer finishes.
Conversely, engraving requires precision and technique. Machine operators adjust parameters like feed rate and depth for desired results. A CNC Rotary Table provides stability for both processes.
Milling involves heavy tool engagement. Tools wear out faster due to friction. Regular checks ensure tool health. Engraving tools face less stress.
They last longer. Sharpness remains crucial. Using a CNC Rotary Table allows better control. It helps optimize tool paths, thus extending tool life. Check tool conditions before operations.
Milling demands varying speeds. Harder materials need slower speeds. In contrast, engraving requires steady, moderate speeds. Maintaining correct RPM ensures quality.CNC Rotary Tables have adjustable speed settings. By setting the correct RPM, operators achieve optimal results. Speed plays a pivotal role in final product quality.
Milling can handle complex shapes. It’s versatile for various materials. Engraving specializes in intricate designs on softer materials. A CNC Rotary Table enhances flexibility.
Its rotation allows multi-angle machining. Achieving complex designs becomes easier. Consider material and design before choosing a method.
Milling setups involve multiple tools and fixtures. Setting up takes time. Engraving, being simpler, requires fewer setup steps. Precision remains vital.
A CNC Rotary Table simplifies setup. With its rotational capabilities, operators reduce re-featuring. Time-saving and efficient, proper setup is fundamental for quality results.
Milling requires precise positioning. Even slight errors affect product quality. Engraving demands even higher accuracy. A CNC Rotary Table ensures high positional accuracy.
With advanced calibration techniques, it offers unparalleled precision. Maintaining equipment health ensures consistent accuracy. Regular maintenance checks are essential.
Milling uses rotary cutters to remove metal. In contrast, engraving uses a pointed tool to carve designs. Milling machines often cost more than engraving ones.
High-speed spindles in CNC rotary tables boost milling unlocking efficiency. You save time but spend more on machine parts like ball screws.
Engraving produces less waste than milling. Precision is key in CNC rotary table operations. Accurate machine calibration reduces scrap metal.
Wasted materials mean lost profits. Aim for precise cuts to save costs.
Milling machines produce more noise. That's due to their powerful motors and cutting actions. Engraving machines, being gentler, make less noise. In a CNC rotary table setup, noise dampening is crucial. Use soundproof booths or wear ear protection during operations.
Milling machines require regular maintenance. Lubrication, part replacements, and calibration are vital. Engraving tools demand less upkeep.
But, for a CNC rotary table, monitor wear and tear. Scheduled checks ensure machine longevity and optimal performance.
Mastering milling takes time. Understanding CNC rotary table operations is essential. Engraving, on the other hand, might be easier to pick up. Both demand attention to detail. Training sessions and hands-on experience enhance skill levels in both techniques.
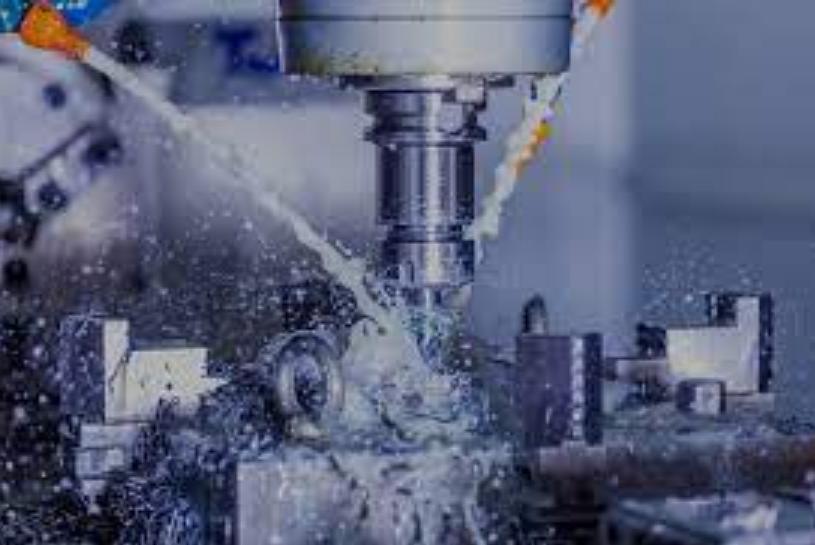

Modern CNC Rotary Tables guarantee an accuracy level within microns. In industries like aerospace, even a slight deviation can result in flawed components. Precision becomes paramount.
With a single setup, you can machine multiple faces of a part. A rotary table allows simultaneous machining on five axes. This capability transforms production processes.
Time-saving becomes evident with CNC Rotary Tables. By reducing manual interventions, you can achieve faster cycle times. In a typical 8-hour shift, production can increase by up to 60%.
Fewer setups mean reduced downtime. CNC Rotary Tables demand fewer tool changes and setups. Over a month, you can save up to 30 hours, enhancing productivity.
Think about intricate designs that were once deemed impossible. With CNC Rotary Tables, intricate patterns and designs become achievable. Industries, especially automotive and medical, benefit immensely.
Adaptability is key in manufacturing. With a CNC Rotary Table, you can handle various part sizes and shapes. Whether dealing with a 2-inch diameter part or a 20-inch one, flexibility remains consistent.
Achieving smooth finishes becomes less challenging. CNC Rotary Tables offer unparalleled surface quality. In sectors like jewelry, this ensures pieces shine brighter and look more refined.
Efficient tool paths lead to reduced tool wear. CNC Rotary Tables optimize these paths, ensuring tools last longer. Over a year, tool replacement costs can drop by up to 40%.

In CNC machinery, proper axis alignment ensures precision. Every CNC Rotary Table demands exact X, Y, and Z alignments. Consistent checks guarantee product quality.
Establishing a zero point is crucial. The CNC Rotary Table needs a starting reference. Calibration begins here. Accurate zero point placement ensures flawless operations every time.
Backlash, the tiny gap between gear teeth, can disrupt accuracy. CNC technicians constantly monitor and adjust for this. Precise backlash correction enhances table performance.
The spindle's rotation must be exact. Minute deviations can compromise product integrity. Regular spindle calibration maintains optimal rotation speed and direction.
Adjusting the tool height is essential. The CNC Rotary Table uses this to determine depth. The right height ensures precise cuts, drilling, and other operations.
CNC operations rely on coordinates. Setting accurate coordinates on the Rotary Table dictates movement precision. Exact coordinates mean error-free products every time.
|
Criteria |
Description |
Importance (1-10) |
Industry Standard |
Deviation Allowed |
Typical Tool Used |
Average Time Taken |
|
Axis Alignment |
Adjusting the X, Y, and Z axes for accuracy. |
9 |
±0.001mm |
±0.005mm |
Laser Aligner |
15 mins |
|
Zero Point |
Setting the machine's origin for operations. |
8 |
Machine Center |
±0.01mm |
Edge Finder |
5 mins |
|
Backlash Correction |
Compensating for slack in machine movement. |
7 |
<0.002mm |
<0.01mm |
Dial Indicator |
20 mins |
|
Spindle Calibration |
Ensuring spindle rotates true and centered. |
8 |
±0.0005mm |
±0.002mm |
Tachometer |
10 mins |
|
Tool Height |
Measuring and setting tool's vertical position. |
9 |
Varies |
±0.01mm |
Tool Presetter |
5 mins |
|
Coordinate Setting |
Defining workpiece's position in machine space. |
8 |
User Defined |
±0.01mm |
Probe |
10 mins |
A Table On Setup And Calibration!

In CNC Rotary Table processes, hardness plays a pivotal role. A higher hardness value means increased wear resistance. For milling, harder materials need robust, durable tools. Conversely, engraving requires precision, even on hard surfaces.
Different tools suit various tasks. Milling involves removing large material portions, demanding stronger tools. Engraving, on the other hand, demands delicate tools for intricate designs. Ensure tool and task alignment for optimal results.
All materials expand with heat. In milling, rapid material removal can generate significant heat. Choose materials with low thermal expansion rates. Engraving minimal material removal means less heat, but material choice still matters.
Some materials cut more easily than others. A high machinability rating indicates ease of cutting. For milling, prioritize materials with higher machinability. Engraving benefits from stable materials that won't chip or fracture.
Rigidity impacts the finish quality. Milling requires materials that can withstand force without deforming. An Engraving benefits from rigid materials, ensuring design fidelity.
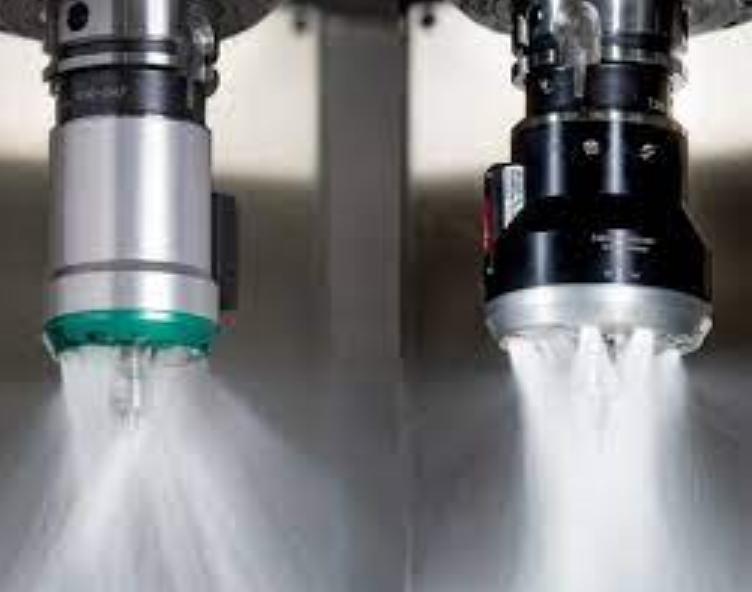

Understand feed rate as the speed at which the cutter moves through the material. A higher feed rate, measured in inches per minute (IPM), boosts productivity.
Determine the depth at which the cutter penetrates the material. Deep cuts require more power but can be efficient. Depths range from 0.01 to 0.25 inches based on material and tool type.
Coolants maintain tool and material temperatures. They reduce friction and extend tool life. Proper coolant flow is crucial. Machines often use gallons per minute (GPM) to measure flow rate.
Strategic toolpaths improve finishes and reduce tool wear. Common strategies include contouring, pocketing, and facing. Selecting the right strategy enhances CNC Rotary Table operations.
Spindle revolutions per minute (RPM) dictate tool rotation speed. Materials like aluminum may require 10,000 RPM, while steel might demand 4,000 RPM. Proper RPM ensures clean cuts and longevity.
In multi-tool operations, rapid tool change minimizes downtime. Advanced CNC Rotary Tables offer tool change speeds of mere seconds. Faster changes lead to efficient production cycles.
Refers to how quickly the machine's axis reaches its maximum speed. Acceleration impacts the quality of intricate designs. Machines with higher G values, like G2 or G3, offer smoother curves and better precision.
Having traversed the CNC Rotary Table landscape, one appreciates its pivotal role in modern machining. For those eager to elevate their machining practices, CNCYANGSEN stands as the beacon. Your next step in achieving unparalleled precision and efficiency lies there. Advance with confidence.