There are two types of machining centers: vertical machining centers and horizontal machining centers.
The main difference between the two is the Z-axis structure. The Z-axis of the horizontal machining center moves horizontally downward, while the Z-axis of the vertical machining center moves vertically downward.
In addition, there are certain differences in their work tables, operation, processing conditions, and prices.
When choosing a machining center, the choice of vertical or horizontal mainly depends on the processing object.
Let's learn together - how to correctly choose vertical and horizontal machining center machine tools.
Machining centers can be divided into vertical machining centers and horizontal machining centers according to the state of the spindle in space.
There are certain differences between these two machining centers:
The main difference between the horizontal machining center and the vertical machining center is the difference in the Z-axis structure.
The Z-axis (spindle axis) of the horizontal machining center moves horizontally downward to complete the processing.
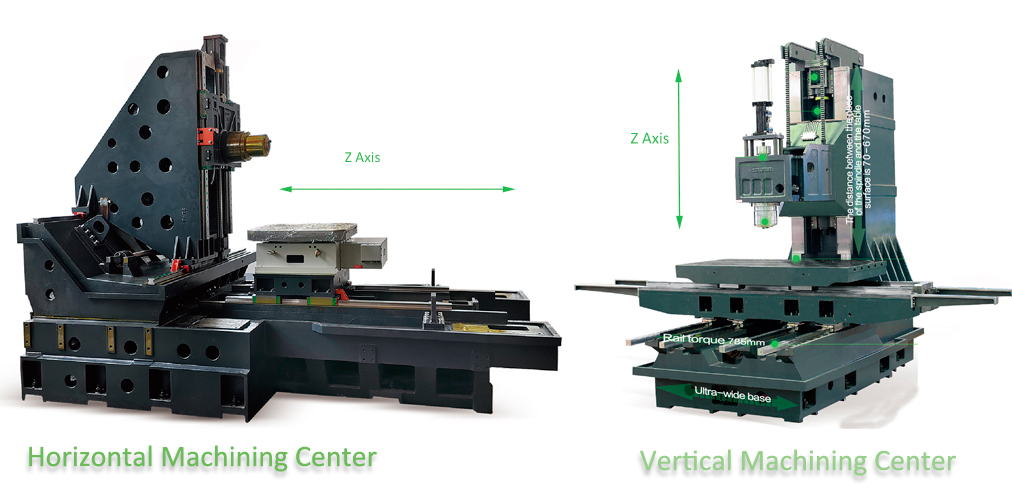
The Z-axis of the vertical machining center moves vertically downward to complete the processing. so the spindle axis of vertical machining centers is in the vertical direction.
The table of the horizontal machining center is only designed to move in the X or Y direction. The table is generally a rotary table with a lattice screw hole table, and it is relatively easy to choose an exchangeable double table.
And generally speaking, horizontal machining centers usually have larger table sizes.
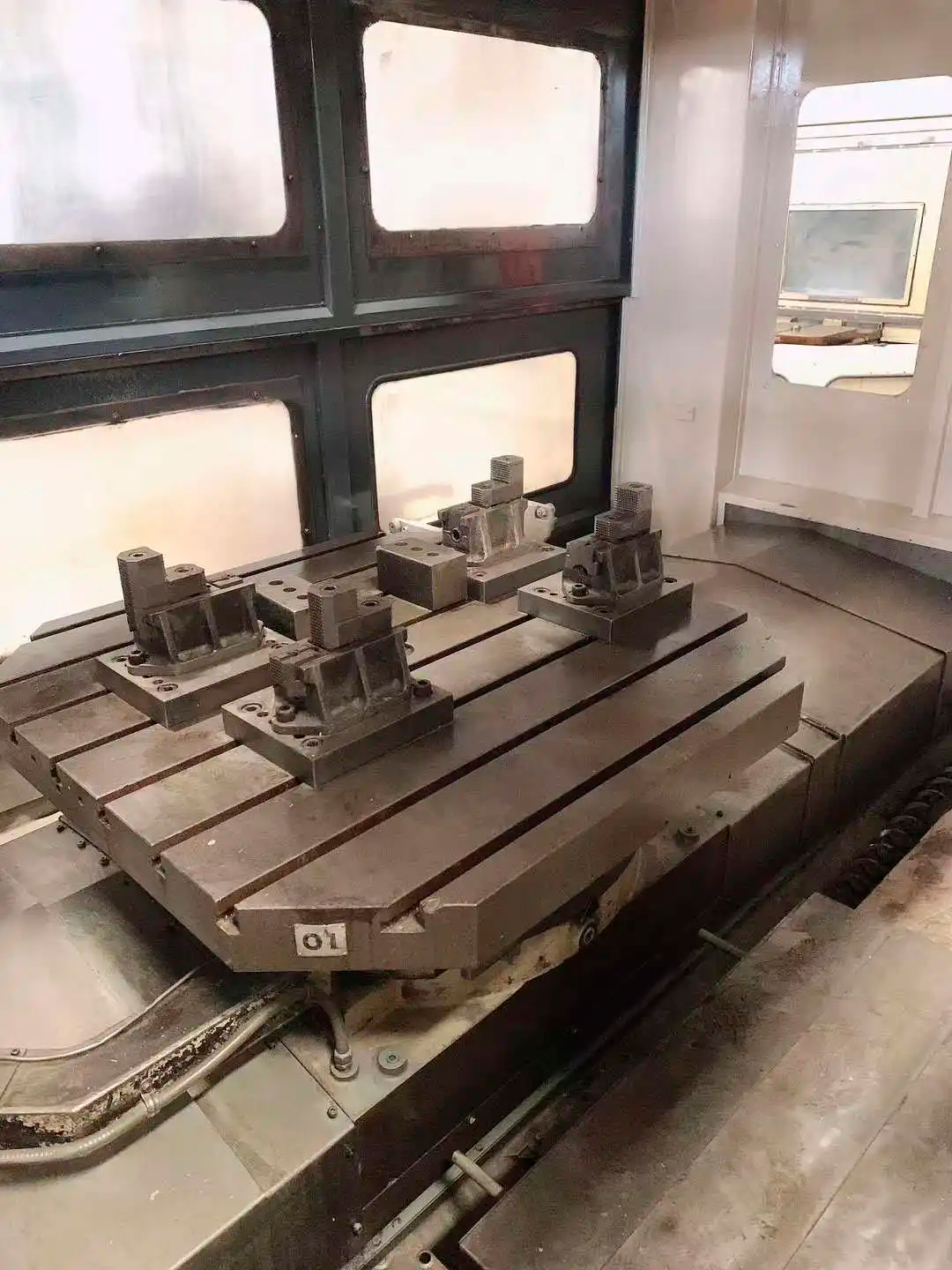

The vertical machining center table is usually a T-slot table with a cross-slide structure. There are two sets of motion mechanisms responsible for the movement in the vertical direction. The X-direction feed table covers the guide rail responsible for the Y-direction feed.
The vertical machining center is easy to clamp, easy to operate, easy to observe the processing situation, and easy to debug the program. Vertical machining centers often use long cylindrical tools called end mills for more precise but shallower cuts on smaller workpieces with a high precision requirement.
The workpieces processed by the horizontal machining center are generally relatively larger, with a higher degree of integration, more difficult to clamp, not easy to monitor the processing process, and relatively difficult to operate and debug.
But under the same table travel of 2 machines, even if it is a large vertical machining center, it is still difficult to compare with a horizontal machining center in terms of processing large workpieces. Large vertical machining centers cannot process parts that are too high.
While large vertical machining centers are relatively easy to be affected by chips when machining concave surfaces, so horizontal machining centers have advantages when machining large workpieces.
The horizontal machining center is easier to remove material and has relatively ideal machining conditions.
When the vertical machining center processes the cavity or the concave surface, the chips are not easy to discharge. In severe cases, the tool will be damaged, the machined surface will be damaged, and the smooth processing will be affected. Special attention should be paid to the installation of the tool and the clamping of the workpiece.

About the chip evacuation management: Why do we need to make sure the chip material does not stick to the inside of the machine cabin, to the fixture, to each other, or to anything really?
The primary concern with chip evacuation is that chips, or particles of the material being machined, can create a fire hazard if they build up and accumulate inside the machine cabin.
They can also cause wear on fixtures and other machine components such as servo motors or spindles. Chips sticking to surfaces inside the machine can interfere with motion or operation, leading to crashes or other mechanical damage.
Finally, chips that get trapped between fixtures and the part can cause defects such as burrs.
For these reasons, it is important to make sure the chip material does not stick to any surfaces inside the machine cabin. To achieve this, operators must evaluate the types of materials being machined and select the best type of coolant for the job, as well as employ effective chip evacuation strategies.
This can include selecting the correct size and shape of cutting tools, adjusting spindle speed, optimizing feed rates and depths, and using appropriate chip breakers.
In addition to all this, it is also important to regularly inspect and clean chips from machines that are in use.
All these steps help to ensure that chip evacuation is efficient and effective.
In general, horizontal machining centers are more expensive than vertical types, because the horizontal machining center is more complex than the vertical machining center in terms of processing technology and structure.
Secondly, there are relatively few manufacturers capable of producing horizontal machining centers. The price of horizontal machining centers with the same processing range is twice as high as that of vertical machining centers.
Vertical machining centers and horizontal machining centers are two different machining centers, and the choice is mainly based on the processing needs:
The vertical machining center occupies a small area, has a simple structure, and has a relatively low price. It is convenient for clamping work, easy to debug the program, and has a wide range of applications, but it cannot process parts that are too high. Parts and other workpieces with a relatively small volume of workpieces.

Vertical CNC machining centers features:
Tool changers for quick and easy tool change, allowing you to set up jobs with multiple tools quickly.
High-speed feed rates for faster production times and improved productivity.
Automated pallet changer that allows you to quickly switch between different jobs without the need for manual intervention.
Advanced control systems
The main advantage of vertical CNC machining centers is that they take up less floor space than horizontal machining centers. This makes them ideal for small shops with limited space. Additionally, vertical machining centers typically have a smaller footprint than horizontal machining centers, making them easier to move around and set up in your shop.
The machining condition of the horizontal machining center is relatively ideal with multiple sides machining. It can complete the machining of the remaining four surfaces except for the mounting surface and the top surface after one clamping. It is more suitable for machining box parts. After adding the angle head, it can realize the pentahedron machining. Generally speaking, if customers need to process a more complex surface finish, they will choose horizontal machining centers.

• Automated pallet changers for increased productivity and flexibility
• Modular tool holders for added versatility
• High-speed spindles for faster cycle times
• Automatic tool changers or multi-tool systems for maximum efficiency
• CNC control system with touchscreen programming for ease of use
There are several reasons to choose horizontal CNC machining centers over vertical CNC machining centers.
First, horizontal machining centers have a larger working envelope than vertical machining centers, which means that they can accommodate larger parts.
Second, horizontal machining centers typically have higher spindle speeds and faster cycle times than vertical machining centers, which makes them more efficient.
Third, horizontal machining centers are better suited for machining parts with a large surface area because they can easily access all sides of the part without having to reposition it.
Finally, horizontal machining centers have the ability to install multiple tools at once and can be equipped with automated pallet changers
When choosing a machining center, whether to choose a vertical machining center or a horizontal machining center mainly depends on what the object to be processed is.