CNC machines have automated and improved many production processes, revolutionizing the industrial sector. In contrast to conventional manual machines, CNC machines are guided by computer programs, enabling accurate and reliable outcomes. This part provides a general overview of how CNC machines have transformed the production environment.
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine is a production equipment that uses digital controls and programming to automate and control the movement of cutting tools or other machinery. It runs using a collection of pre-programmed instructions called G-code, which establishes the exact motions and uses of the CNC machine tools.
Cutting, milling, drilling, turning, 5-axis machining, and shaping are just a few of the production activities that CNC machines can do with great precision and reproducibility.
Because they are designed to execute jobs that were previously done manually, CNC machines are more effective, accurate, and dependable. These machines are commonly utilized to create components and products with complicated designs and precise tolerances in various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, furniture, and medical.
A CNC machine requires several steps to operate. Here is a step-by-step description of what happens:
To generate a 2D or 3D model of the component you want to make, use computer-aided design (CAD) software. Indicate the size, characteristics, and any other relevant information.
Use computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software to translate your design into G-code, which CNC machines use. The CAM program determined the tool paths and needed cutting operations, creating toolpaths.
Set up your CNC machine under the detailed instructions that the manufacturer has supplied. This might include mounting the workpiece firmly, installing and positioning the cutting instruments, and connecting the required wires.
Transfer the resulting G-code program to the CNC machine's control system from your PC. Typically, a USB drive, network connection, or other means of data transmission enabled by your computer are used.
To guarantee that the CNC machine begins operations from the appropriate reference locations, precisely establish the work and tool offsets. This procedure aids in precisely aligning the tool's initial location with the workpiece.
To ensure everything is configured correctly, run a test program before machining the fundamental component. This makes the cutting processes, toolpaths, and machine motions go as planned.
Once you are happy with the outcomes of the test program, start the machining procedure. Typically, this entails selecting the "start" button on the software interface or the control panel of the CNC machine.
During machining, watch the CNC machine to ensure everything goes as planned. Pay heed to any alerts or cautions pointing to a problem with the cutting tools or the machine.
Carefully remove the final object from the CNC machine after completing the machining process. Watch out for any hot or jagged surfaces.
Debris must be cleared from the CNC machine, and cutting tools must be stored safely. To guarantee the machine's optimum efficiency and lifespan, maintain it often following the manufacturer's recommendations.
It's crucial to remember that specific CNC machines could have distinctive features and operating processes, so for comprehensive instructions tailored to your particular machine type, always consult the manufacturer's paperwork and recommendations.
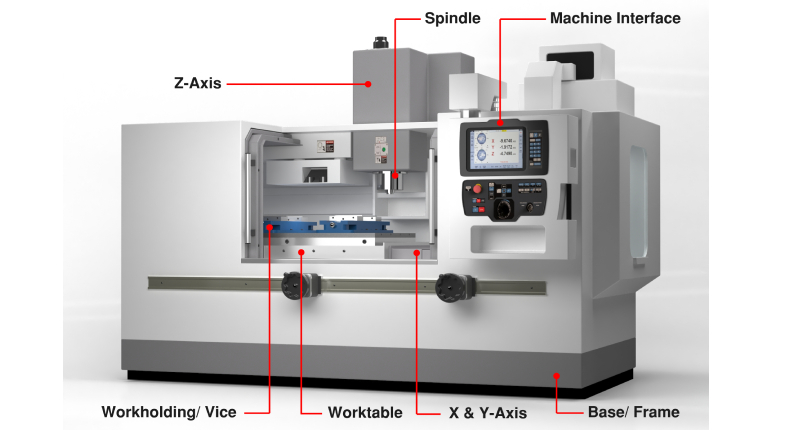
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines automate and regulate the movement of cutting tools or other equipment using hardware and software components. The stages in the procedure are as follows-
Software for computer-aided design (CAD) is used to create the component or item that will be produced. The CNC program's foundation is a digital model of the item created by CNC software.
The CNC machine's control system or computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software receives the loaded CNC software. The CAD/CAM software defines the Toolpath generation, feed rates, and other machining parameters to produce the CNC program. G-code, a standardized programming language for CNC machines, is typically used to create the program.
The cutting tools are correctly put into their corresponding tool holders, and the workpiece is firmly fixed on the worktable or spindle of the CNC machine. The workpiece and CNC machine tools may be accurately located using the machine's sensors and measuring systems.
A CNC machine must be set up correctly to operate accurately and efficiently. Here are some essential procedures for configuring a CNC machine-
When installing the CNC machine, adhere to the manufacturer's instructions to ensure appropriate alignment, connection of power and utilities, and grounding.
Perform calibration operations to ensure the machine is aligned correctly and its axes are pointed in the right direction. This entails inspecting and correcting the machine's worktable, spindle, and other components for squareness, levelness, and parallelism.
Install and arrange the tool holders or cutting tools in the spindle or tool magazine of the machine. Ensure the devices are securely fastened and positioned following the machine's instructions.
Mount the workpiece firmly on the machine's worktable, chuck, or fixture. Use the proper clamps, vises, or other fixturing techniques to hold the workpiece firmly and securely throughout the machining process.
By precisely determining the workpiece's location about the machine's coordinate system, establish the reference or zero point for the workpiece. Edge finders, probes, or other measuring methods may be used.
The machine's control system has the CNC program put into it. The machine follows the G-code-defined instructions as it runs the software step-by-step. The cutting tools are moved along specific axes (X, Y, and Z) by the machine's motors and actuators, and numerous operations are carried out on the workpiece. The machine's control system translates the G-code directives into precise motions and actions.
By communicating with the machine's motors, the CNC controller system synchronizes the motions of the cutting tools and workpiece. These motors, powered by servo systems or stepper motors, precisely and accurately move the machine's axes. The control system constantly checks the axes' location and speed to ensure they are driving as intended by the software.
It may include feedback systems like encoders or sensors to maintain precision and modify the cutting settings while using the machine. The machine can monitor the position, speed, and forces used during cutting operations using these feedback systems, which enable real-time modifications and correction.
The final product is removed from the machine during the machining operation. Additional post-processing stages like deburring, surface polishing, or inspection may be carried out depending on the needs.
By employing CNC equipment, manufacturers may attain high precision, accuracy, and reproducibility levels in their manufacturing processes. Compared to conventional manual machines, CNC machines provide several benefits, such as higher productivity, lower labor costs, and the capacity to create elaborate and complicated components.
CNC machines are a piece of flexible and essential equipment in various sectors, from the automotive and aerospace to electronics and carpentry. This is due to their machine automation and programmability.

A critical first step in beginning CNC machining is selecting the appropriate CNC machine. When choosing a CNC machine, keep the following things in mind-
Establish the specific duties and procedures you want using the CNC machine. Different machines are created for varied purposes like milling, turning, routing, or laser cutting. Select a device that is appropriate for your intended purpose.
Think about the dimensions and nature of the workpieces you want to manufacture. CNC equipment comes in a range of sizes and weight capabilities. Make sure the machine you choose can manage the materials you'll be working with, such as metal, wood, plastic, or composites, and accommodate the size of your workpiece.
Determine the degree of accuracy and precision needed for your work. Different degrees of precision are available with CNC machines, and things like repeatability, positioning accuracy, and surface polish may define these levels. Select a machine that satisfies your required accuracy standards.
Establish a spending plan for purchasing a CNC machine, considering the purchase price and ongoing maintenance and operating costs. Consider how much the tools, software, machine shop, and other extras or attachments you'll need for your particular applications will cost.
Analyze the availability of the manufacturer's or supplier's technical assistance, training materials, and documentation. Ensure you can access dependable support resources for CNC maintenance, software upgrades, and troubleshooting.
CNC machines are essential to manufacturing numerous vehicle components because they allow accurate and effective production. Several uses include-
Engine blocks, cylinder heads, crankshafts, and camshafts are all precisely and accurately made using CNC equipment.

CNC machines manufacture brake calipers, steering knuckles, steering components, and other vital chassis system elements.
Dashboard panels, door trims, grilles, and emblems are just a few examples of interior and exterior parts made using CNC machines to guarantee consistent quality and fit.
Molds die, and CNC machines produce tooling for automobile production processes.
The aerospace sector mainly depends on CNC machines to manufacture intricate and exact components. Several uses include-
Aluminum, titanium, and composite materials are utilized to make structural components such as fuselage pieces, wing ribs, brackets, and landing gear sections using CNC machines.
CNC machines, including housings, compressor blades, and turbine blades, produce critical engine parts with sophisticated geometries and precise tolerances.
Molds, jigs, fixtures, and other equipment needed to manufacture and assemble aeronautical components are made using CNC machines.
The aerospace sector uses CNC machines to build prototypes and research projects, allowing iterative design and validation procedures.
Artists and designers can now produce Intricate and exact works thanks to CNC machines, which have changed the art and design sector. Several uses include

Intricate 3D shapes may be carved out of various materials using CNC machines, including foam, stone, metal, and wood.
Custom furniture, ornamental panels, and delicate architectural features are made with meticulous precision machining.
High-quality signs, lettering, and logos for companies, occasions, and architectural projects are created using CNC machines.
Jewelry made from precious metals and gemstones, including rings, pendants, and earrings, is produced using CNC machines.
Safety should always come first while using CNC equipment. When using CNC machines, safety must always come first. Following safety procedures reduces hazards and aids in creating a secure working environment for workers and anyone around the equipment. To guarantee a safe operating environment, use the following safety precautions-
Wear the proper PPE, such as safety glasses, hearing protection, and armor. When working with sharp objects or materials, use gloves.
Ensure that all moving components, including belts, pulleys, and rotating spindles, are securely guarded to avoid unintentional contact. Install safety fences or enclosures around the equipment to shield users and onlookers from possible risks.
Learn where the emergency stop switch or button is on the machine and how to use it. In case of any emergency or unforeseen circumstances, be prepared to utilize it.
Make sure the workstation is well-ventilated, mainly if you're dealing with substances that emit dust, fumes, or gases. Use air filtration or extraction devices as needed.
Ensure that everybody using CNC machines has the appropriate training on using the equipment, safety precautions, and emergency procedures. Keep current with the most recent safety recommendations and best practices.
The combination of additive manufacturing, automated manufacturing and robotics, artificial intelligence and machine learning, and additive manufacturing will significantly enhance CNC technology in the future.
CNC processes will run more efficiently, reduce manual labor, and make continuous production possible. Complex and bespoke products will be possible thanks to CNC machining and additive manufacturing.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning will improve overall performance, forecast tool wear, and optimize CNC operators. These developments will improve CNC machining productivity, design adaptability, and decision-making.
It is anticipated that if CNC technology develops even further, industrial processes will become more productive, precise, and customizable. CNC machines can unleash the power of precise manufacturing in both extensive- and small-scale production facilities.
Individuals and companies may fully use the capabilities of CNC machines to accomplish their production objectives and spur innovation in the years to come by learning the fundamentals, experimenting with methodologies, and keeping up to date with new trends.
Q- What are the key advantages of using CNC machines?
Increased accuracy, efficiency, automation, repeatability, and the capacity to work with complicated geometries are some of the main benefits of employing CNC machines.
Q- Can CNC machines be used for both large-scale and small-scale production?
You can utilize CNC machines for both large- and small-scale manufacturing. They can handle different production quantities and are scalable.
Q- How long does it take to learn CNC programming?
The time needed to learn CNC programming might vary based on past experience, the difficulty of projects, and the speed at which each person learns. Gaining proficiency might take a few weeks to a few years.
Q- What are the common materials that can be machined with CNC?
Various materials may be processed using CNC machines, including metals (such as aluminum, steel, and titanium), wood, polymers, composites, and foam.
Q- Are CNC machines suitable for hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts?
Yes, new learners and DIY enthusiasts may use CNC machines. The availability of numerous CNC machine sizes and kinds, from tiny desktop machines to bigger industrial-grade machines, makes them affordable for amateurs and enthusiasts with various demands and spending capacities.