In the fast-paced world of precision machining, the role of VMC (Vertical Machining Center) Axis maintenance cannot be overstated. As manufacturing processes become more intricate, the need for precise and efficient machining has never been greater. This article delves into the heart of machining excellence, exploring the significance of VMC Axis maintenance in achieving and sustaining success.
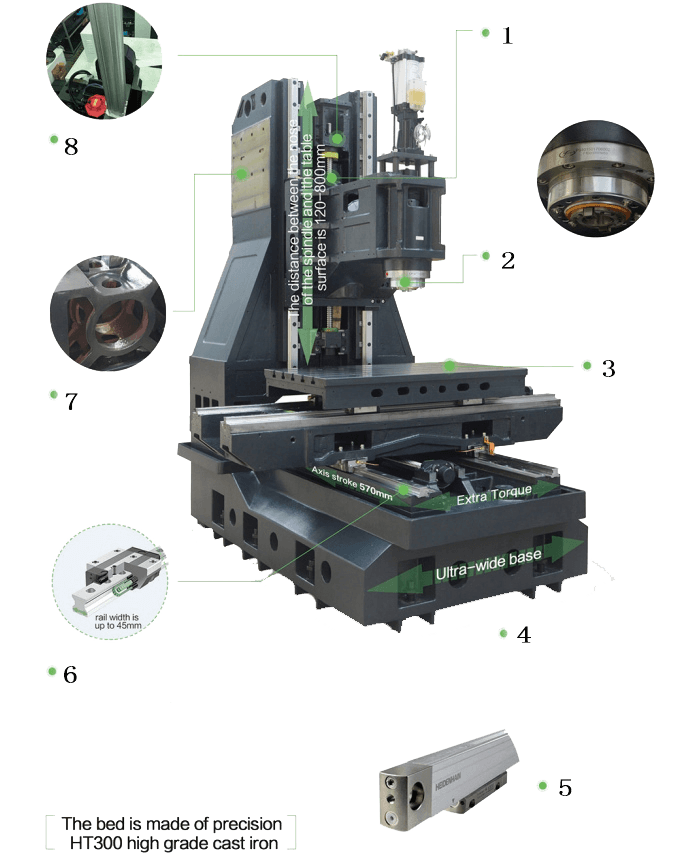
The VMC (Vertical Machining Center) Vertical Machine Axis is a critical component within the machining domain, specifically in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Vertical Machining. This axis refers to the orientation of the machining center spindle or cutting tool that moves vertically along the Z-axis. To comprehend its significance, let's break down its key components:
Spindle: The core of the Vertical Machine Axis, the spindle holds the cutting tool and rotates it to perform various machining operations.
Z-Axis Assembly: Responsible for vertical movement, the Z-axis assembly ensures precise positioning of the spindle about the workpiece.
Control System: The brain behind the operation, the control system interprets programmed instructions and orchestrates the movement of the VMC Axis components.
Feedback Mechanism: Sensors and feedback systems provide real-time data on the position and movement of the spindle, allowing for adjustments to ensure accuracy.
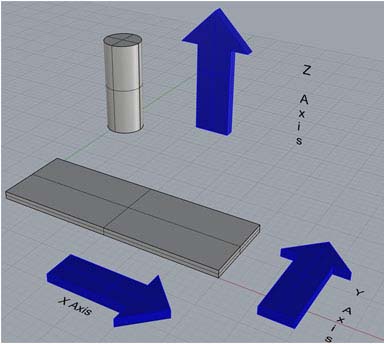
Calibration is the heartbeat of precision machining, and mastering the calibration process is paramount for achieving consistent and accurate results with CNC Vertical Machining Tools. Calibration refers to the adjustment of the machine's settings to align it with specified standards. In precision machining, the slightest deviation can result in dimensional inaccuracies, jeopardizing the quality of the final product.
Calibrating CNC Vertical Machining Tools ensures that each operation, from milling to drilling, maintains consistent accuracy. This is especially critical when working on intricate components that demand precise dimensions.
Proper calibration contributes to the optimal performance of cutting tools. By aligning the machine accurately, wear on tools is minimized, extending their lifespan and reducing the frequency of tool replacements.
Calibration acts as a safeguard against errors that may arise due to machine drift, temperature variations, or other environmental factors. It serves as a proactive measure to mitigate the impact of external influences on machining accuracy.
CNC Vertical Machining Tools encompass a diverse array of instruments designed for specific machining applications. Understanding these tools and their functionalities is fundamental to the calibration process.
End Mills: Versatile cutting tools used for various milling operations, end mills come in different types, including flat end mills, ball end mills, and corner radius end mills.
Drill Bits: Essential for creating holes in workpieces, drill bits vary in size and design to accommodate different hole specifications.
Face Mills: Ideal for facing and squaring operations, face mills consist of multiple cutting edges and are suitable for removing large amounts of material.
Taps and Dies: Used for threading operations, taps create internal threads, while dies create external threads.
Reamers: Precision tools designed to create smooth, accurate holes with specific diameters. They are crucial for achieving tight tolerances.
Choosing the right CNC Vertical Machining Tools is a critical aspect of achieving optimal performance, and this decision is closely tied to the calibration process.
Different materials demand specific tools. Calibrating the machine to accommodate the characteristics of materials, whether metals, plastics, or composites, ensures efficient cutting and minimal tool wear.
Understanding the geometry of tools is vital. Calibration should factor in the tool's geometry to ensure that it engages with the workpiece in a manner that produces the desired result.
Tool coatings, such as TiN (Titanium Nitride) or TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride), affect tool performance. Calibrating for specific coatings optimizes cutting speed and minimizes friction, contributing to extended tool life.
Adjusting the machine's RPM (Revolutions Per Minute) and feed rates based on tool specifications is crucial. Calibrating these parameters ensures the tool operates within its recommended performance range.
A. Importance of Regular Calibration Stress the importance of regular calibration for ensuring the seamless operation of VMC Axis. Discuss the potential consequences of neglecting calibration in terms of precision and efficiency.
B. Step-by-Step Guide to Vertical machining center Axis Calibration Provide a detailed step-by-step guide on how to calibrate VMC Axis. Include best practices, common challenges, and solutions to empower readers to conduct effective calibrations.
C. Common Issues and Troubleshooting Address common issues that may arise during VMC Axis operation and provide troubleshooting tips. This section aims to equip readers with the knowledge to identify and resolve potential problems swiftly.
4th Axis Machining represents a paradigm shift in precision and versatility within the realm of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining. Unlike traditional 3-axis machining, the 4th Axis introduces an additional rotational axis (usually around the X, Y, or Z-axis), unlocking new dimensions of complexity and precision.
The introduction of a 4th Axis provides rotational freedom to the workpiece, enabling machining operations from multiple angles. This rotational capability allows for the creation of intricate features and contours that would be challenging or impossible with conventional 3-axis machining.
With 4th Axis Machining, toolpaths become more dynamic. Tools can now follow the curvature of a workpiece, resulting in smoother surfaces and more efficient material removal. This enhanced toolpath control is particularly advantageous in sculpting, engraving, and complex part production.
One of the primary advantages of 4th Axis Machining is the ability to machine multiple sides of a workpiece without manual repositioning. This not only saves time but also ensures alignment accuracy across all sides, crucial for intricate components requiring precision on all surfaces.
4th Axis Machining excels in creating complex contours and intricate geometries. This is particularly valuable in industries such as aerospace and medical, where components often feature intricate shapes and precise detailing.
The ability to machine multiple sides of a workpiece without repositioning significantly reduces set-up time. This is a critical advantage, especially in high-volume production scenarios where efficiency is paramount.
The dynamic toolpath capabilities and simultaneous machining of multiple sides contribute to increased productivity. This is especially beneficial for manufacturers looking to optimize their machining processes and meet demanding production schedules.

VMC (Vertical Machining Center) Machining Tools form the backbone of precision manufacturing, encompassing a diverse array of instruments designed to shape, cut, and carve materials with accuracy. Understanding the intricacies of these tools is fundamental to achieving machining excellence.
Flat End Mills: Ideal for flat surfaces and general milling operations.
Ball End Mills: Suited for contouring and sculpting, creating rounded features.
Corner Radius End Mills: Used for milling rounded corners, combining flat and ball end mill characteristics.
Twist Drills: Commonly used for creating holes in various materials.
Center Drills: Provide a starting point for larger drills or create a divot for lathe centers.
Shell Mills: Designed for facing large areas, removing material efficiently.
Indexable Face Mills: Utilize replaceable inserts for cost-effective maintenance.
Taps: Used for threading internal holes in materials.
Dies: Create external threads on cylindrical objects.
Straight Flute Reamers: Ideal for enlarging and finishing existing holes.
Spiral Flute Reamers: Improve chip evacuation and enhance surface finish.
Choosing the right VMC Machining Tools is a critical decision that directly impacts the outcome of machining operations. Considerations must be made based on the specific application and material properties.
Different materials require specific tooling. For example:
Carbide tools excel in cutting hard materials like metals.
High-speed steel tools are suitable for softer materials such as plastics.
Select tools based on the intended machining operation:
End mills with varying geometries for milling and contouring.
Drill bits for creating precise holes.
Face mills for facing large surfaces.
Consider coatings to enhance tool durability and performance:
TiN (Titanium Nitride) coatings for general-purpose applications.
TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride) coatings for increased heat resistance.
Understanding tool geometry is crucial:
Flute count and helix angle impact chip evacuation and surface finish.
Cutting-edge geometry influences the type of cuts the tool can perform.
In the ever-evolving landscape of precision machining, staying abreast of the latest innovations in VMC Machining Tools is essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
Tools designed for machining composite materials, offering precision in aerospace and automotive industries.
Integration of sensors and monitoring capabilities for real-time data on tool wear, enabling predictive maintenance.
Advanced coatings for improved wear resistance, reduced friction, and extended tool life.
Tailored tools for specific applications, designed to address unique machining challenges.
Embark on a journey of precision and innovation with CNC Yangsen. Our website is your gateway to a world where machining excellence meets cutting-edge technology. Explore our comprehensive range of VMC (Vertical Machining Center) solutions, state-of-the-art CNC Vertical Machining Tools, and revolutionary 4th Axis Machining Techniques.
At CNC Yangsen, we don't just provide tools; we offer a roadmap to operational brilliance. Elevate your machining processes with our expertise in VMC Axis maintenance, calibration techniques, and the latest advancements in VMC Machining Tools. The toolbox of excellence awaits, tailored to propel your operations to new heights of efficiency and success.
