CNC milling machines are devices used in manufacturing to precisely cut and shape materials. These machines operate based on pre-programmed computer software, which controls the movement of the tools and machinery. This precision is crucial for creating detailed parts and components.
CNC milling machines are essential in modern manufacturing. They ensure high levels of accuracy and repeatability, which are vital for producing complex parts in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics. Their reliability and efficiency have transformed production processes, reducing the need for manual intervention.
The evolution from manual milling to CNC milling represents a significant technological advancement. Initially, milling required skilled operators to manually control the cutting tools. With the advent of computer numerical control (CNC), the process became automated, improving precision and productivity. This shift has allowed for more intricate designs and faster production times.
CNC milling machines consist of many parts, with around fifteen key components. Important parts include the CNC controller, spindle, work table, tool changer, and coolant system. These components work together to perform precise machining tasks.
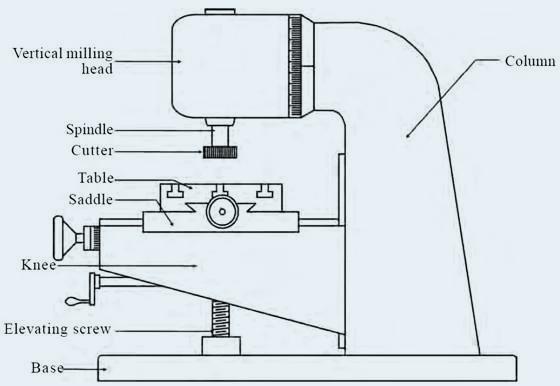
Each part of a CNC mill plays a vital role in its operation. The CNC controller processes commands, the spindle holds and rotates the cutting tools, and the work table supports the machining material. The tool changer allows quick tool swapping, while the coolant system prevents overheating. Together, these parts ensure accurate and efficient manufacturing.
The base of a CNC milling machine serves as its foundation. It supports the entire machine, ensuring stability during operation. The base is typically constructed from cast iron or welded steel, materials chosen for their strength and ability to absorb vibrations. This construction helps maintain precision during milling by reducing movement and vibration.
The column of a CNC mill provides structural support for other components, such as the spindle and the arm. It is integrated with the base to form a rigid framework, ensuring stability and precision. The column is often made of the same materials as the base, like cast iron or steel, to maintain strength and vibration absorption consistency. Its design ensures that the machine can handle the stresses of milling without compromising accuracy.
The knee is an adjustable vertical support on a CNC milling machine. It allows for the work table and saddle movement along the Z-axis. This adjustability is crucial for positioning the workpiece at the correct height for machining. The knee is connected to the saddle and the table, providing a stable platform for vertical adjustments. Its robust construction ensures that it can support the weight and movement of the workpiece and table during milling operations.
The saddle in a CNC milling machine is a crucial component responsible for horizontal movement. It is the main support for the work table, allowing it to move along the X and Y axes. This horizontal movement mechanism is essential for positioning the workpiece accurately under the cutting tool. By sliding back and forth, the saddle ensures that the milling process can cover the necessary area on the workpiece with precision.
The work table of a CNC milling machine is the surface where workpieces are mounted. It provides a stable platform for the materials being machined. The table moves along both the X and Y axes, enabling precise control over the position of the workpiece. This dual-axis movement is crucial for intricate machining tasks, allowing the tool to accurately reach various points on the workpiece. The work table is equipped with T-slots or clamps to secure the workpieces firmly, ensuring stability during milling operations.

The power feed mechanism in a CNC milling machine automates the movement of the saddle and work table. This automatic movement control is vital for maintaining consistent feed rates and ensuring smooth operation. By eliminating the need for manual adjustments, the power feed mechanism enhances precision and efficiency in machining. Consistent feed rates are critical for achieving high-quality finishes and maintaining dimensional accuracy. The automated system also reduces operator fatigue, allowing longer and more complex machining processes without compromising precision.
The spindle is a crucial part of a CNC milling machine. It holds and rotates the cutting tools, ensuring they are precisely aligned and rotated at the correct speed to perform various machining tasks. The spindle's speed and stability directly affect the quality of the milling process, making it a vital component for achieving high precision.
There are different types of spindles, each with specific specifications. Belt-driven spindles are common and offer a range of speeds, making them versatile for various applications. Direct-drive spindles provide higher precision and faster speeds, making them suitable for intricate and high-speed machining. Additionally, gear-driven spindles are robust and can handle heavy-duty operations, making them ideal for cutting tough materials.
The tool holder is another essential component that secures tools in the spindle. It ensures the cutting tools are firmly attached, preventing any movement during machining. This stability is crucial for maintaining precision and achieving high-quality finishes on the workpiece.
There are various types of tool holders, each designed for specific applications. Collet chucks are widely used for their versatility and ability to hold a range of tool sizes. End mill holders provide a secure grip for end mills, ensuring stability during heavy cutting. Hydraulic tool holders use hydraulic pressure to clamp the tools, offering excellent precision and damping capabilities. Each type of tool holder is selected based on the specific requirements of the machining task.
The tool changer is an automated system that allows for quick swapping of tools during the milling process. This system enhances productivity by reducing the time needed to change tools manually. The machine can automatically switch between different cutting tools with a tool changer, allowing continuous and efficient machining.
The benefits of using a tool changer are significant. It reduces downtime, increases production speed, and allows for more complex machining operations without manual intervention. This automation boosts efficiency and ensures consistent precision throughout the machining process.
The control panel is the user interface for operating a CNC milling machine. It provides operators access to all machine functions, enabling them to control the milling process. The panel typically includes a display screen, buttons, switches, and knobs. These components allow users to input commands, adjust settings, and monitor the machine's performance. The control panel is designed to be intuitive, making it easy for operators to navigate and manage the machine's operations effectively.
The CNC controller is often called the brain of the CNC milling machine. It processes the G-code commands that dictate the machine's movements and operations. The CNC controller interprets these commands and sends signals to the motors and drives, ensuring precise execution of machining tasks. It coordinates the machine's actions, managing the sequence of operations and maintaining accuracy. The machine could not perform automated and precise milling tasks without the CNC controller.

Motors and drives are critical components in the motion control system of a CNC milling machine. They are responsible for moving the machine's axes according to the instructions from the CNC controller. Two main types of motors are used in CNC machines: stepper motors and servo motors.
Stepper motors are known for their simplicity and ability to provide precise control over position. They move in discrete steps, which makes them ideal for applications where accuracy is crucial. Servo motors, on the other hand, offer higher performance and can provide continuous motion with real-time feedback. They are preferred for applications requiring high speed and precision.
Drives are the interface between the CNC controller and the motors. They receive signals from the controller and convert them into electrical power to drive the motors. The combination of motors and drives ensures smooth and accurate movement of the machine's axes, enabling precise machining operations.
The coolant system in a CNC milling machine plays a vital role in cooling and lubricating during machining. It consists of several components that work together to ensure efficient cooling.
• Nozzles: Direct the coolant flow precisely to the cutting area.
• Pump: Circulates the coolant throughout the system.
• Reservoir: Stores the coolant for reuse.
• Filters: Remove debris from the coolant to maintain its effectiveness.
Maintenance of the coolant system involves regularly checking the coolant level, cleaning the nozzles, and replacing the filters. Proper cooling and lubrication are essential to prevent overheating and reduce friction, which can extend the lifespan of both the machine and the cutting tools.
The chip management system is designed to remove metal shavings produced during machining. Efficient chip removal is crucial for maintaining machine performance and safety.
• Chip Augers: Transport chips away from the cutting area.
• Chip Conveyors: Move chips to a collection bin or disposal area.
• Chip Trays: Collect chips for easy removal.
Effective chip management prevents the accumulation of metal shavings, which can damage tools and interfere with the machining process. The chip management system enhances efficiency and safety by keeping the work area clear of debris.
The lubrication system automatically lubricates the moving parts of a CNC milling machine, ensuring smooth operation and reducing wear.
• Pump: Distributes lubricant to various machine components.
• Reservoir: Stores the lubricant.
• Distribution Lines: Carry the lubricant to different parts of the machine.
Regular lubrication is crucial for the longevity and performance of the machine. The system minimizes friction and wear on moving parts, which helps maintain precision and reduces the risk of breakdowns. Proper lubrication also contributes to the overall efficiency of the machining process.
Feedback systems in CNC milling machines are crucial for ensuring precision and accuracy. They consist of encoders and sensors that provide real-time data on the position and movement of machine components.
• Encoders: Measure the position of the machine's axes and send feedback to the CNC controller.
• Sensors: Monitor parameters such as speed, temperature, and tool position.
These components work together to maintain high precision during machining. By continuously monitoring and adjusting the machine's movements, feedback systems help achieve consistent accuracy, which is essential for producing high-quality parts.
Probing systems are on-machine measurement tools used to verify the dimensions and alignment of workpieces during the machining process. They provide several benefits for quality control.
• Touch Probes: Detect the surface of the workpiece and measure its dimensions.
• Laser Probes: Use laser technology for non-contact measurement.
These probing systems allow for quick and accurate measurement directly on the machine, reducing the need for manual inspection. This capability enhances quality control by ensuring that each part meets the required specifications before removing it from the machine. Probing systems also help detect errors early, allowing immediate corrections and reducing waste.
Safety features are integral to CNC milling machines. They ensure operator safety and prevent accidents. These features include guards, emergency stops, and interlocks.
• Guards: Enclose moving parts to protect operators from contact.
• Emergency Stops: Provide a quick way to halt the machine in an emergency.
• Interlocks: Prevent the machine from operating if safety guards are not in place.
These safety features are designed to protect operators from potential hazards. Guards prevent accidental contact with moving parts, while emergency stops allow immediate shutdown in dangerous situations. Interlocks ensure that the machine cannot be operated without all safety measures, further enhancing the safety of the work environment.
|
Component |
Function |
Benefits |
|
Base |
Provides stability and support for the entire machine |
Ensures stable and accurate machining |
|
Spindle |
Holds and rotates cutting tools |
Enables precise cutting and shaping |
|
Tool Holder |
Secures tools in the spindle |
Maintains tool stability for high-quality finishes |
|
Work Table |
Supports and moves the workpiece along X and Y axes |
Allows precise positioning of the workpiece |
|
Control Panel |
User interface for operating the machine |
Simplifies machine operation and monitoring |
|
Motors |
Move the machine's axes |
Ensures precise axis movements for accurate machining |
|
Feedback Systems |
Monitor and adjust machine movements for precision |
Achieves high precision and accuracy |
|
Probing Systems |
Measure dimensions and alignment of workpieces during machining |
Enhances quality control and reduces errors |
|
Coolant System |
Cools and lubricates cutting tools |
Prevents overheating and reduces friction |
|
Chip Management System |
Removes metal shavings |
Maintains machine performance and safety |
|
Lubrication System |
Automatically lubricates moving parts |
Reduces wear and extends machine lifespan |
CNC milling machines consist of various critical parts, including the base, spindle, tool holder, and control systems, all essential for precision machining. Technological advancements continue to enhance these machines, introducing more automation and improved accuracy. Future trends suggest further integration of smart technologies and enhanced feedback systems. CNC milling machines play a vital role in modern manufacturing, enabling the efficient production of complex and precise parts. Their ongoing development promises even greater capabilities, solidifying their importance in the industry.